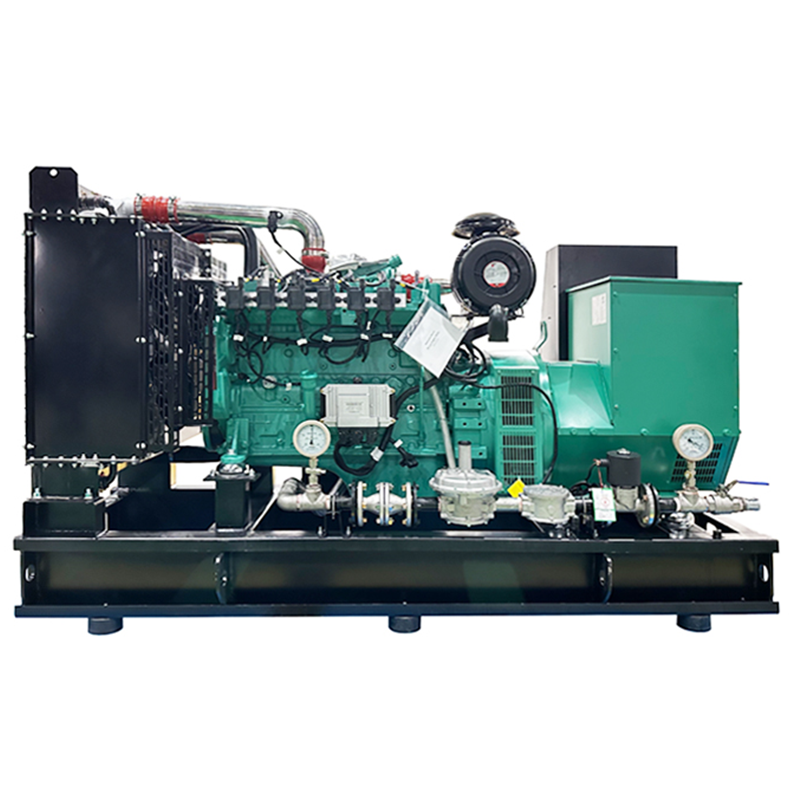
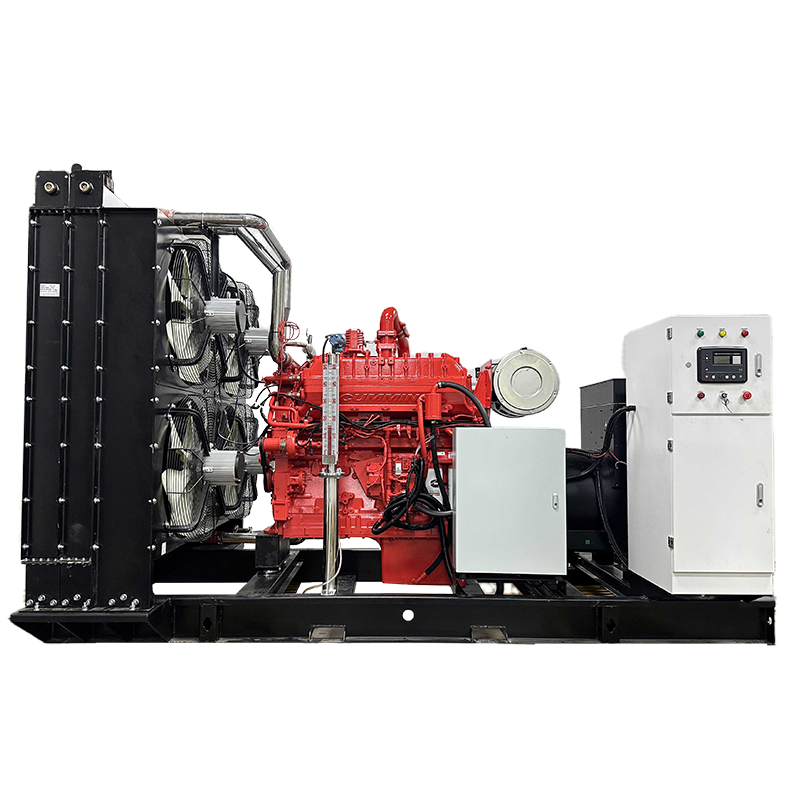
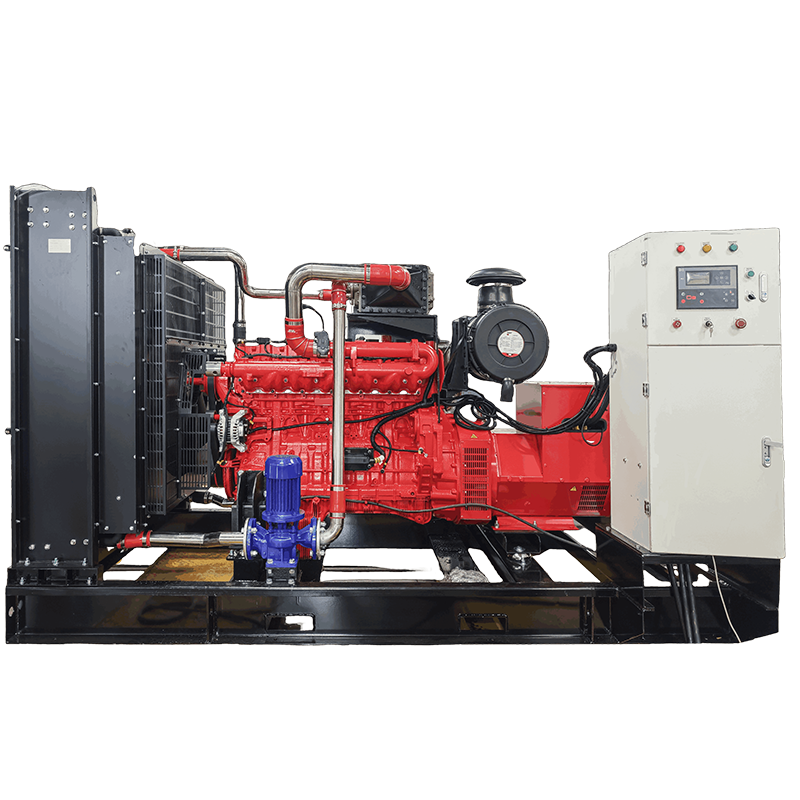
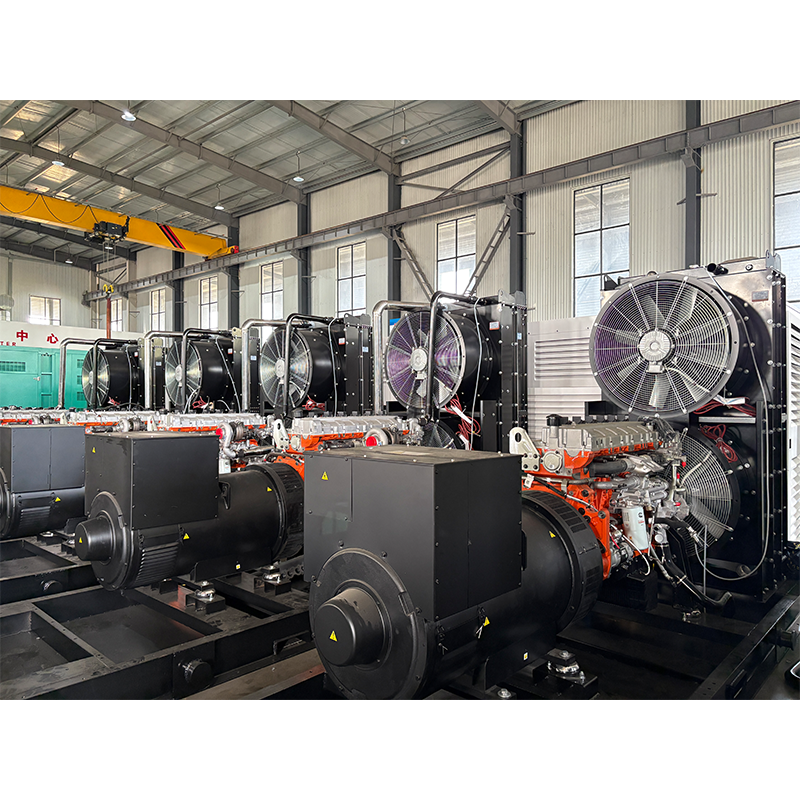
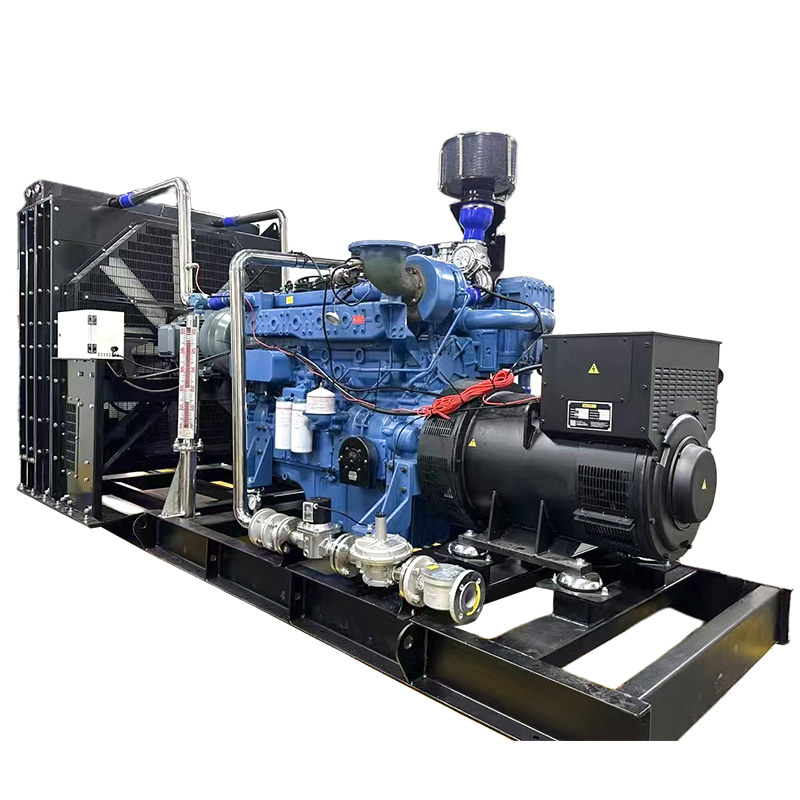
Biogas generator set
Working Principle
Biogas goes through pretreatment (desulfurization, dehydration, pressure stabilization) to remove impurities and avoid equipment corrosion.
Purified biogas mixes with air in ratio, entering the engine cylinder.
The mixture is compressed, ignited by spark plug; high-temp/pressure gas pushes piston to drive crankshaft (thermal→mechanical energy).
Crankshaft rotates generator rotor to generate electricity (mechanical→electrical energy); control system adjusts biogas supply and speed for stable output.
- Overview
- Recommended Products
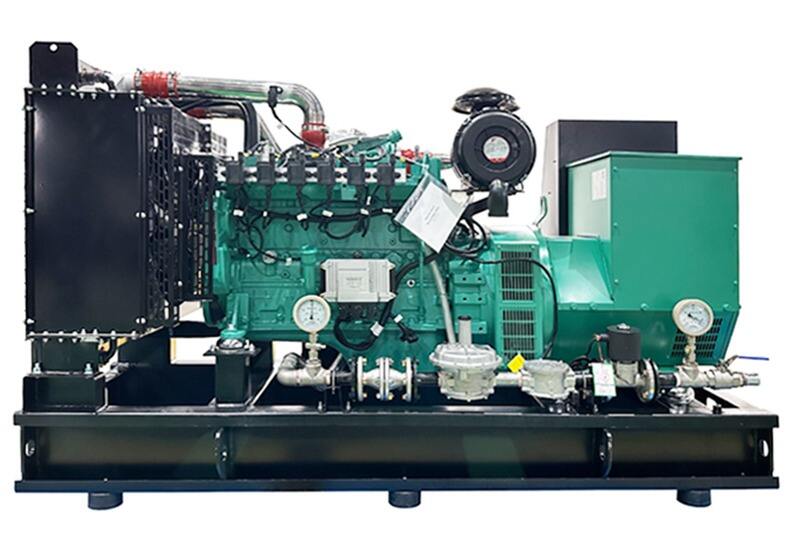
Core Features
Fuel Adaptability: Handles biogas from different sources (methane 50%-70%), pretreatment reduces impurity impact.
Eco-cycle: Consumes biogas (cuts greenhouse gas), recovered waste heat aids biogas production (e.g., fermenter heating).
Structure: Anti-corrosion engine parts fit biogas combustion, extending service life.
Pros & Cons
Pros: Low fuel cost (from waste), low carbon emission, "waste-energy-fertilizer" cycle.
Cons: Biogas output depends on fermentation conditions (temp, raw materials); power stability relies on gas source; regular pretreatment maintenance needed.
Typical Applications
Agriculture: Livestock farms, straw processing stations (waste recycling).
Environmental: Food waste treatment plants, sewage plants (supporting biogas projects).
Rural Areas: Distributed power stations (stable power for remote villages).






