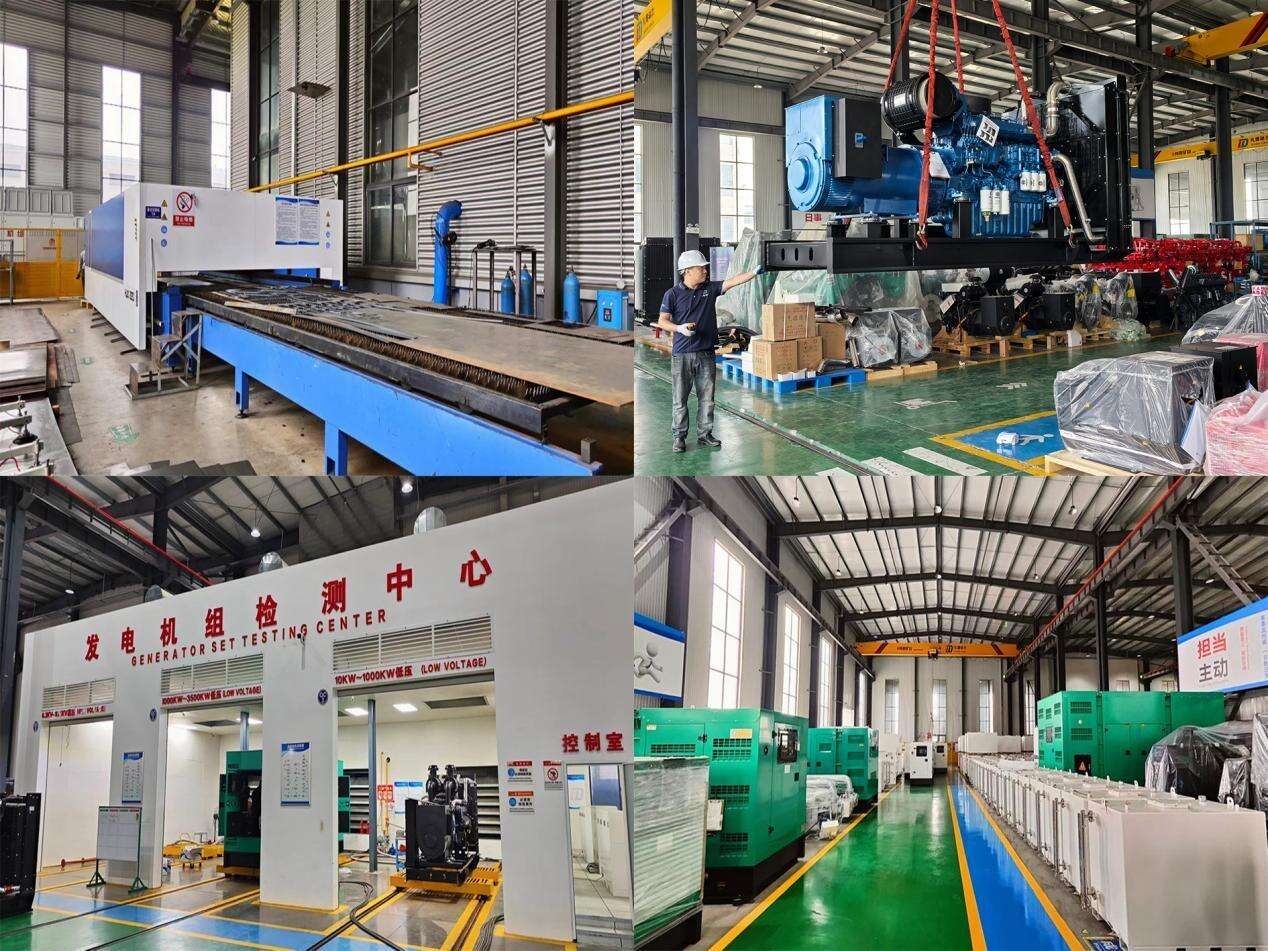
With biogas generators, one of the most common issues is lower power output than anticipated. This is often the result of biogas quality and engine part wear. Biogas needs a specific methane content of 50% to 70% to combust properly. If the power generating biogas methane is below this threshold it is usually due to poor digestion in the biogas digester pertaining to non optimal temperature and imbalanced feedstock digestion.
Wear and tear of other engine parts such as spark plugs or fuel injectors could be another culprit. Parts that combust fuel to generate power in the engine get clogged with carbon deposits due to incomplete combustion which then causes fuel inefficient combustion. In this case, the first step is to check if there is methane content with a gas analyzer. If there is, adjust the digester feedstock ratio and temperature of 35°C for mesophilic digestion. For worn parts, you should replace spark plugs every 500 hours of operation and clean fuel injectors with a professional cleaning agent.
Unstable Operation and Frequent Shutdowns
Having a biogas generator that often shuts down and runs intermittently can be incredibly annoying for those who need continuous electricity. Inconsistent supplies of biogas and defective pressure regulators can cause this to occur. In a digester, biogas production can be inconsistent and cause production to fluctuate if there are feedstocks that need to be added, or if there are gas collection system leaks. To add to this, gas pressure that drops below a certain threshold causes an engine generator to stutter and stop.
Another source for this problem are malfunctioning pressure regulators. The biogas engine pressure regulator controls how much biogas is allowed to enter the engine, and if a biogas engine pressure regulator is malfunctioning, the flow of biogas becomes unsteady and could cause the system to malfunction. To remedy ongoing system unsteadiness, the first thing to do is repair the gas collection system leaks and maintain a schedule for biogas production to eliminate the reserve of feedstocks to prevent production instability. Inspect pressure regulators biogas flow components for damage or blockages so the system can run continuously. If a regulator is damaged, replace it with a quality pressure regulator to biogas system to ensure optimized continuous flow.
High Emission Levels
Biogas is a cleaner fuel than diesel but some generators still produce excessive pollutants like NOx and CO. Underdeveloped combustion systems of older biogas engines and poor air-fuel mixing cause this issue. If biogas burners receive too little air, incomplete combustion produces excessive CO. Conversely, too much air produces NOx due to high combustion chamber temperatures.
Contribution to this problem can come from older engines that lack current emission control technologies. Emission control can be accomplished simply by optimizing air-fuel ratio. Most biogas generators have an air intake valve—adjust this to ensure 10:1 biogas volumetric ratio. Emission analyzers can provide precise measurement of the system and control the air-fuel mixture to the point that emissions fall under the prescribed regional standards. Catalytic converters designed for biogas engines can be installed on older engines to reduce pollutants. Gas pollutants can be converted to harmless water vapor and CO2. Engine maintenance will also keep emissions down, for example, by opening air passage after 200 hours of operation.
Difficulty Starting the Generator
As the weather changes or the generator sits for long periods, users often find it difficult to start the biogas generator. Low biogas pressure, low temp engines, and dead batteries are the most likely culprits. Starting issues due to low biogas pressure are caused by low pressure. Without sufficient pressure, the system struggles to send gas into the engine combustion chamber, and ignition becomes almost impossible.
The cold weather has a negative impact on combustion. In fact, the biogas cold engine combustion and the inefficient generator cranking may sound like it is on yet is in combustion. Centered ignition dead batteries are also a frequent cause if the generator hasn’t been used for weeks. Starting issues may be resolved by first identifying the source of the problem in the biogas system. If the pressure is low, assume the digester has to run for 24 to 48 hours. In cold weather, 1 to 2 hours of warm up using an engine block heater. For dead batteries, charge the portable charger for 4 to 6 hours, and check the ignition system to make sure it is working.
Fuel System Components and Corrosion
Corrosion of biogas generator components like pipes or valves is a silent problem star deteriorating biogas generators. Biogas contains a small percentage of hydrogen sulfide. When biogas and H₂S is in an enclosed system with moisture a chemical reaction occurs and becomes corrosive. If early biogas generator components are not repaired or replaced what results is a biogas generator with a corrosive H₂S leakage problem. Eventually they cause biogas generator and fuel system operational issues and costly repairs.
In an attempt to eliminate corrosion the first thing to do is to install biogas H₂S removal systems on biogas pipelines. The system should eliminate H₂S gas to less than 20 ppm before biogas fuels are used. Have a system in place to regularly check for fuel H₂S corrosion. Weak fuels systems in corrosion moisture should be drained or has accelerated corrosion.Enabled H₂S gas in moisture has to be biogas corroding moisture within the system should be drained and dried.








 Hot News
Hot News